
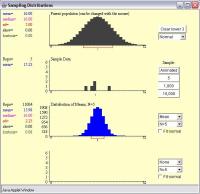
Generate a sample distribution of (n 5) and hit the animate button. Try to draw a distribution that is not even close to being Normal. Hit clear lower 3 and repeat for a population with a Custom distribution. coming ut? Hit the 10.000 sample button and see what hannans How 3. How does it compare to the that sample does it compare to the original mean and standard deviation of the population? wn Keen hittinn the animats button many times and lnk at the shane of the distribution that falls out Now hit the 5 button to do 5 sampls at a time What distribution do does it compare to the original distribution? How does it compare to the original mean and standard deviation of the population? otice. What distribution do you notice coming out? Hit the 10,000 sample button and see what happens. Not hit the 5 button to do 5 samples original distribution? ) and hit the animate button, You will see 5 random data points are chosen and the mean and standard deviation are shown. For a population with a Skewed distribution, generate a sample distribution of (n= button many times and look at the shape of the distribution that falls out. (htp:///stat_sim/sampling dist/index.html) Create Thread and answer the the following questions in your new discussion post 1. Repeated game playing, adaptive data compression, sequential investment in the stock market, sequential pattern analysis, and several other problems are viewed as instances of the experts' framework and analyzed from a common nonstochastic standpoint that often reveals new and intriguing connections.Transcribed image text: Launch the Samplng Distibutions applet. The central theme is the model of prediction using expert advice, a general framework within which many related problems can be cast and discussed. Yet, prediction algorithms can be constructed that work well for all possible sequences, in the sense that their performance is always nearly as good as the best forecasting strategy in a given reference class.

Unlike standard statistical approaches to forecasting, prediction of individual sequences does not impose any probabilistic assumption on the data-generating mechanism. This important new text and reference for researchers and students in machine learning, game theory, statistics and information theory offers the first comprehensive treatment of the problem of predicting individual sequences. We also analyze other algorithms, which tie together several different previous approaches including follow-the-leader, exponential weighting, Cover’s algorithm and gradient descent. Our analysis shows a surprising connection to follow-the-leader method, and builds on the recent work of Agarwal and Hazan. The main new ideas give rise to an efficient algorithm based on the Newton method for optimization, a new tool in the field. We propose several algorithms achieving logarithmic regret, which besides being more general are also much more efficient to implement. This mirrors what has been done for the special cases of prediction from expert advice by Kivinen and Warmuth, and Universal Portfolios by Cover. In this paper, we give algorithms that achieve regret O(log(T)) for an arbitrary sequence of strictly convex functions (with bounded first and second derivatives). Given a sequence of convex functions $f_0, f_1, \ldots, f_T$, we study the problem of sampling from the Gibbs distribution $\pi_t \propto e^)\), for an arbitrary sequence of T convex cost functions (of bounded gradients), with respect to the best single decision in hindsight.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
